Artificial Intelligence
ChatGPT’s Market Share Falls to 68 Percent as Gemini Closes the Gap
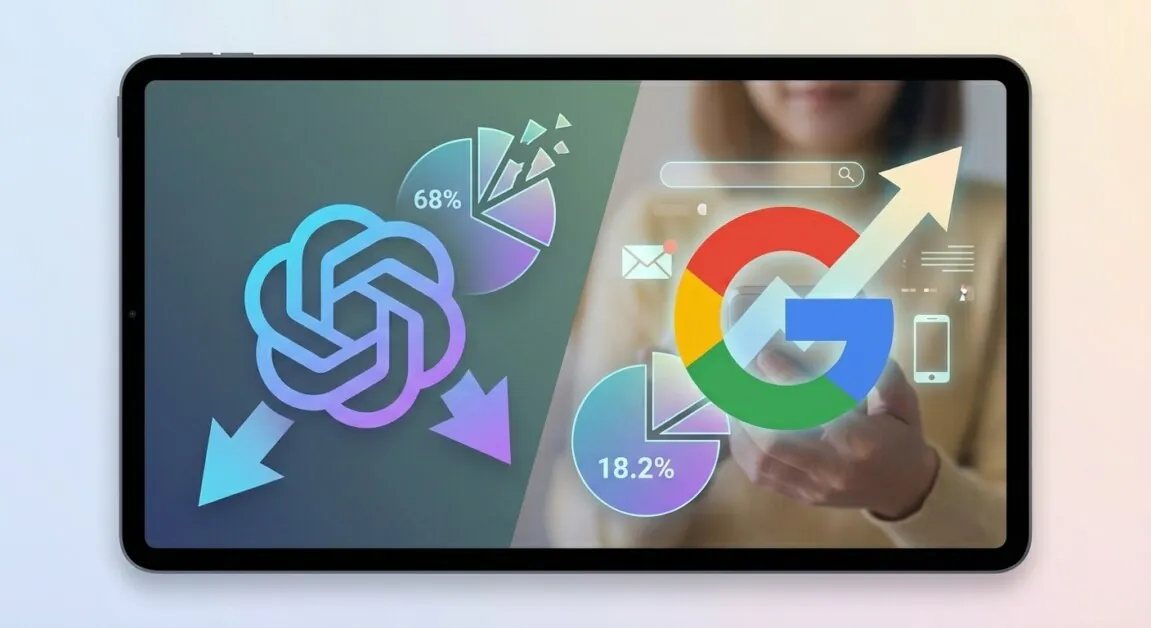

ChatGPT’s grip on the generative AI market is slipping faster than its user base is growing. New Similarweb data shows the chatbot’s share of website traffic dropped from 87.2 percent to 68 percent over the past year—a 19-point decline even as absolute users climbed to 800 million weekly.
Google Gemini is the primary beneficiary. The platform surged from just 5.4 percent market share a year ago to 18.2 percent today, more than tripling its position while ChatGPT shed nearly one-fifth of its relative dominance. The shift suggests the initial ChatGPT hype wave is settling into a more competitive phase where Google’s infrastructure and distribution advantages are paying off.
The data, released December 25, captures a market in transition. Grok from xAI grew modestly to 2.9 percent. DeepSeek holds steady at around 4 percent. Claude and Perplexity each hover near 2 percent, while Microsoft Copilot remains flat at 1.2 percent.
What’s Driving Gemini’s Surge
Two factors stand out. First, Google’s aggressive model releases throughout 2025 have closed the capability gap with ChatGPT. The Gemini 3 Flash launch made the latest model the default across Google’s ecosystem, and the company’s December “code red” response from OpenAI suggests the competitive pressure is real.
Second, Nano Banana Pro—Google’s image generation model built on Gemini 3 Pro—has driven significant adoption. The model’s ability to render legible text directly in images addresses a persistent weakness in AI image generators, and its integration across Gemini, Google Search, NotebookLM, and Workspace tools gives it distribution ChatGPT can’t match.
Gemini’s user base grew from 450 million monthly active users in July to 650 million by October—a 44 percent increase over three months. The growth rate dwarfs ChatGPT’s roughly 5 percent expansion during the same period. Perhaps more telling: Similarweb found that referral traffic from Gemini to external websites grew 388 percent year-over-year, compared to 52 percent for ChatGPT.
The Android Advantage
Google’s control of the Android operating system provides a distribution channel OpenAI can’t replicate. Similarweb data shows twice as many US Android users engage with Gemini through the operating system directly compared to the standalone app. That built-in access means Gemini doesn’t need to convince users to download anything—it’s already there.
Apple’s decision to partner with OpenAI for Siri integration was supposed to offset this advantage, but the implementation has been slow. Meanwhile, Google has made Gemini the default assistant on Android devices, ensuring that hundreds of millions of users encounter it without seeking it out.
The integration story extends to Google’s broader ecosystem. Gemini runs in Gmail, Docs, Slides, and Search. Enterprise customers using Google Workspace get AI assistant features without additional subscriptions. ChatGPT requires users to leave their existing workflows; Gemini increasingly appears within them.
ChatGPT’s Monetization Problem
The market share decline compounds an existing challenge for OpenAI: converting free users to paying subscribers. Despite 800 million weekly users, only about 5 percent pay for ChatGPT Plus or higher tiers—roughly 40 million subscribers. And paid subscriptions have plateaued across major European markets since May, with no recovery in sight.
The combination is concerning. A shrinking market share suggests ChatGPT is losing the attention battle. Flat subscription growth suggests it’s also losing the monetization battle. If both trends continue, OpenAI’s revenue growth could stall even as its infrastructure costs escalate.
OpenAI isn’t standing still. The company’s “code red” response to Gemini 3 produced GPT-5.2 in under a month—the fastest major model iteration in the company’s history. The release reclaimed benchmark leads that Gemini had briefly seized, and CEO Sam Altman has reportedly delayed planned advertising features to focus resources on product quality.
But model quality may matter less than distribution. ChatGPT wins head-to-head comparisons on many benchmarks, yet Gemini is growing faster because it’s embedded in platforms people already use. The lesson from browser wars and social media contests applies here too: being better isn’t always enough when the competition is more convenient.
The Fragmentation Phase
Some analysts view the current moment as the beginning of a fragmentation phase for AI assistants. The initial ChatGPT monopoly is giving way to a market where multiple players hold meaningful share—similar to how social media evolved from Facebook dominance to a landscape including Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter.
Claudе and Perplexity both saw triple-digit growth in 2025, with Perplexity up 370 percent year-over-year and Claude up 190 percent. Neither yet commands significant market share, but their growth rates suggest the market is far from settled. Grok’s modest gains show that even relatively new entrants can carve out positions.
For users, fragmentation brings benefits. Competition drives feature development and keeps pricing in check. For investors betting on a single AI chatbot winner, the data suggests a more complicated future. ChatGPT remains the leader by a wide margin, but that margin is narrowing quarter by quarter.
What This Means
The 19-point market share drop over 12 months is the clearest signal yet that ChatGPT’s first-mover advantage is eroding. OpenAI built an extraordinary product that defined a category, but Google brought scale, distribution, and patience. Gemini wasn’t better than ChatGPT at launch; it’s catching up because Google keeps iterating and has more surfaces to reach users.
The next year will test whether OpenAI can stabilize its position. The company has cash from recent funding rounds, a strong enterprise business, and a product development pace that matches or exceeds competitors. But it doesn’t have an operating system, a search engine, or a productivity suite with billions of existing users.
ChatGPT’s absolute numbers remain staggering—no other AI product has achieved anything close to 800 million weekly users. The question is whether those users represent a stable foundation or a high-water mark as alternatives proliferate and the novelty fades.
Daily visits across all AI tools actually dipped slightly in recent weeks, Similarweb noted. The generative AI market may be entering a phase where growth comes from taking share rather than expanding the pie. In that contest, distribution matters as much as capability—and on distribution, Google has advantages OpenAI can’t easily match.